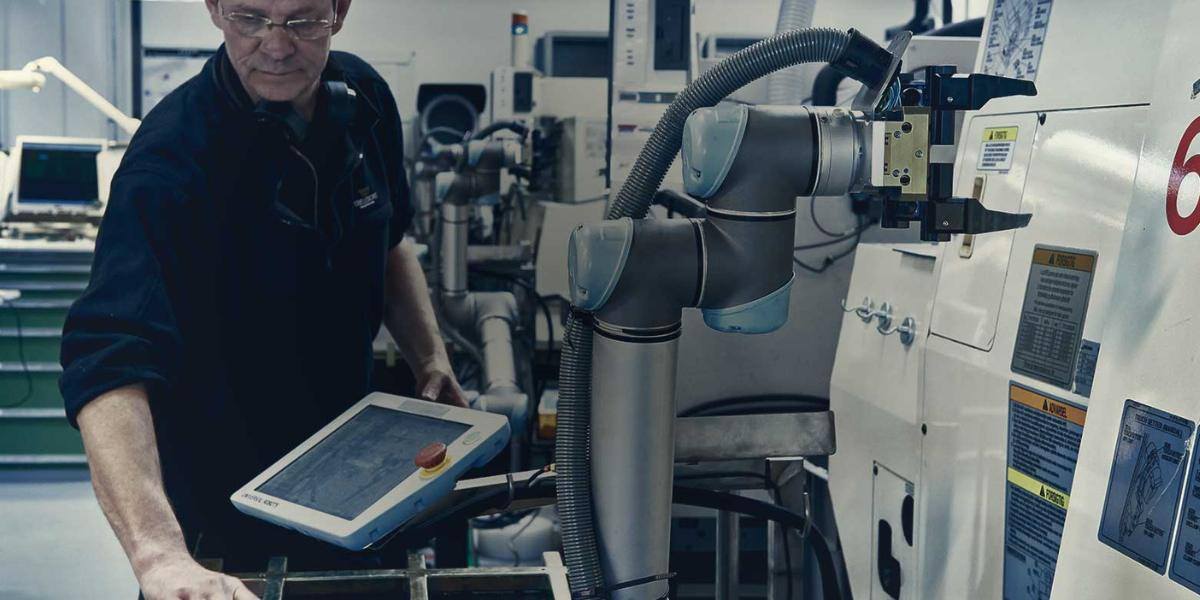
Automation with collaborative robots (also known as "cobots") is a growing trend in the manufacturing sector. However, cost remains a major obstacle for many businesses. So, how much does a collaborative robot actually cost, and what factors determine its price? In this article, we explore the key elements that influence the cost of such an investment and how companies can achieve a tangible return on investment (ROI).
What Is a Collaborative Robot?
A collaborative robot is a robotic arm designed to work safely alongside human operators. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots are lighter, more flexible, and designed for easy integration into shared work environments. These robots are ideal for various applications, such as assembly, palletizing, and quality control.
The Price of a Collaborative Robot
The price of a collaborative robot varies depending on several factors, including project size, task complexity, and the specific needs of the business. On average, a standalone cobot costs between $50,000 and $90,000. However, this price only covers the robot itself and does not include additional elements needed for programming and integration. Application kits and other options are not part of the standard offering and must be purchased separately.
A typical cobot purchase includes:
- A robotic arm
- A controller
- A programming pendant (teach pendant)
- A power cable and a cable connecting the arm to the control unit
- Documentation
Total Cost of a Robotic Cell
Purchasing a collaborative robot is just one part of the overall investment. When factoring in the full integration of the robotic cell— which may include sensors, grippers, conveyors, and vision systems—the total cost can easily reach between $150,000 and $300,000, or even more.
Factors That Influence the Cost
- Project Complexity: Automating simple processes (e.g., palletizing) is generally less expensive than more complex applications, such as automated quality control using machine vision.
- Customization: The more tailored the solution, the higher the cost. Adding specific functionalities like a vision system or a data acquisition software increases expenses.
- Integration & Training: Implementing a cobot into a production line requires specialized expertise and time, adding significant costs. Additionally, training staff to operate the system is a crucial factor to consider.
How to Maximize Return on Investment?
A key aspect of decision-making is calculating ROI. On average, a robotic project becomes profitable within three years after implementation. Beyond financial returns, cobots also offer non-quantifiable benefits, such as improved workplace conditions for employees. Acquiring a collaborative robot should not be seen as just a purchase but as a strategic project that requires detailed planning.
Before getting started, it is essential to understand your specific needs, how the robot will integrate into your existing processes, and the overall integration costs. The pre-engineering phase is a crucial step to ensure the project's success. Careful planning will help you optimize ROI and avoid unexpected costs.